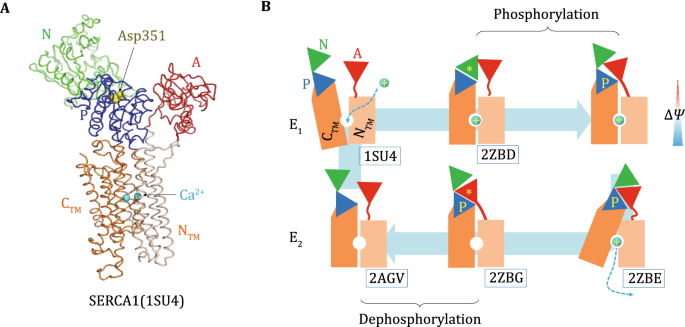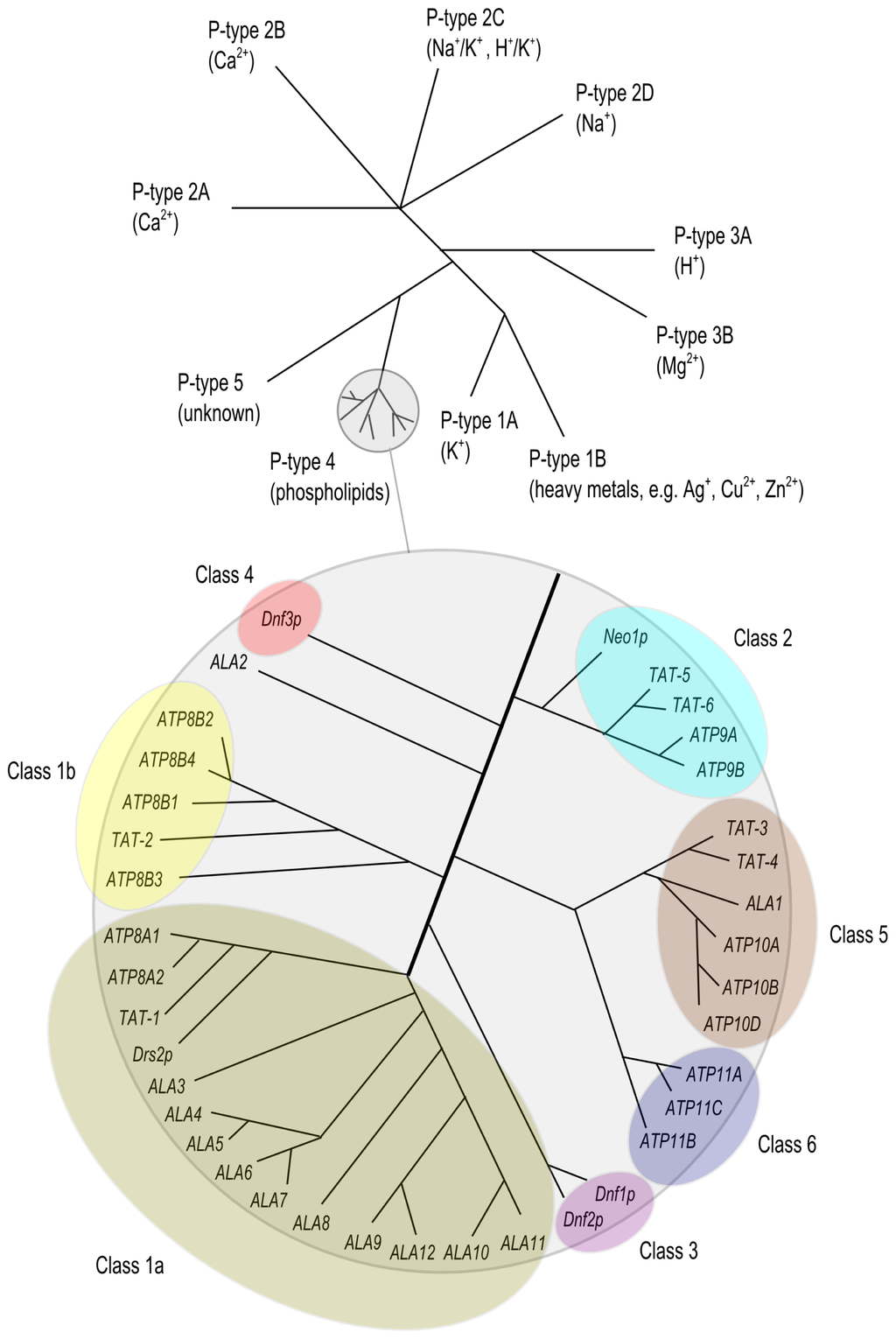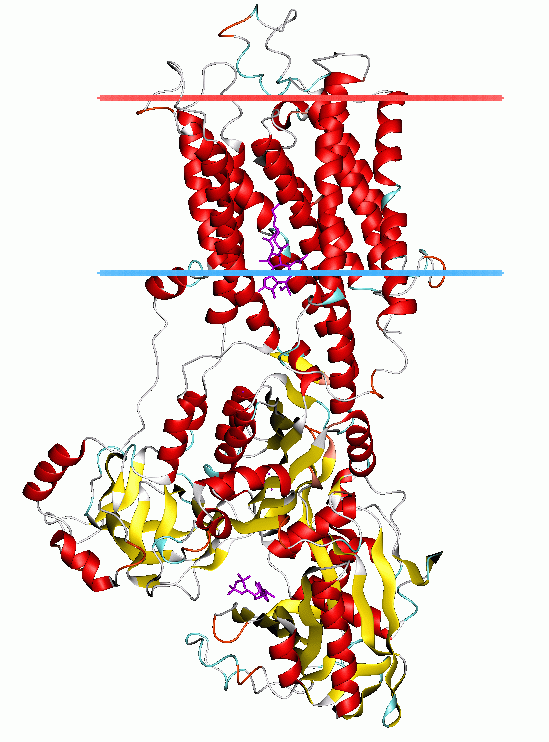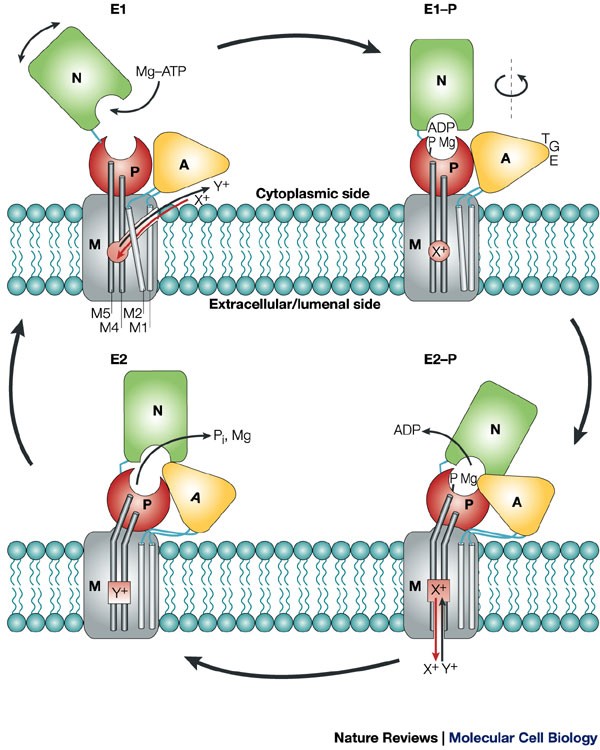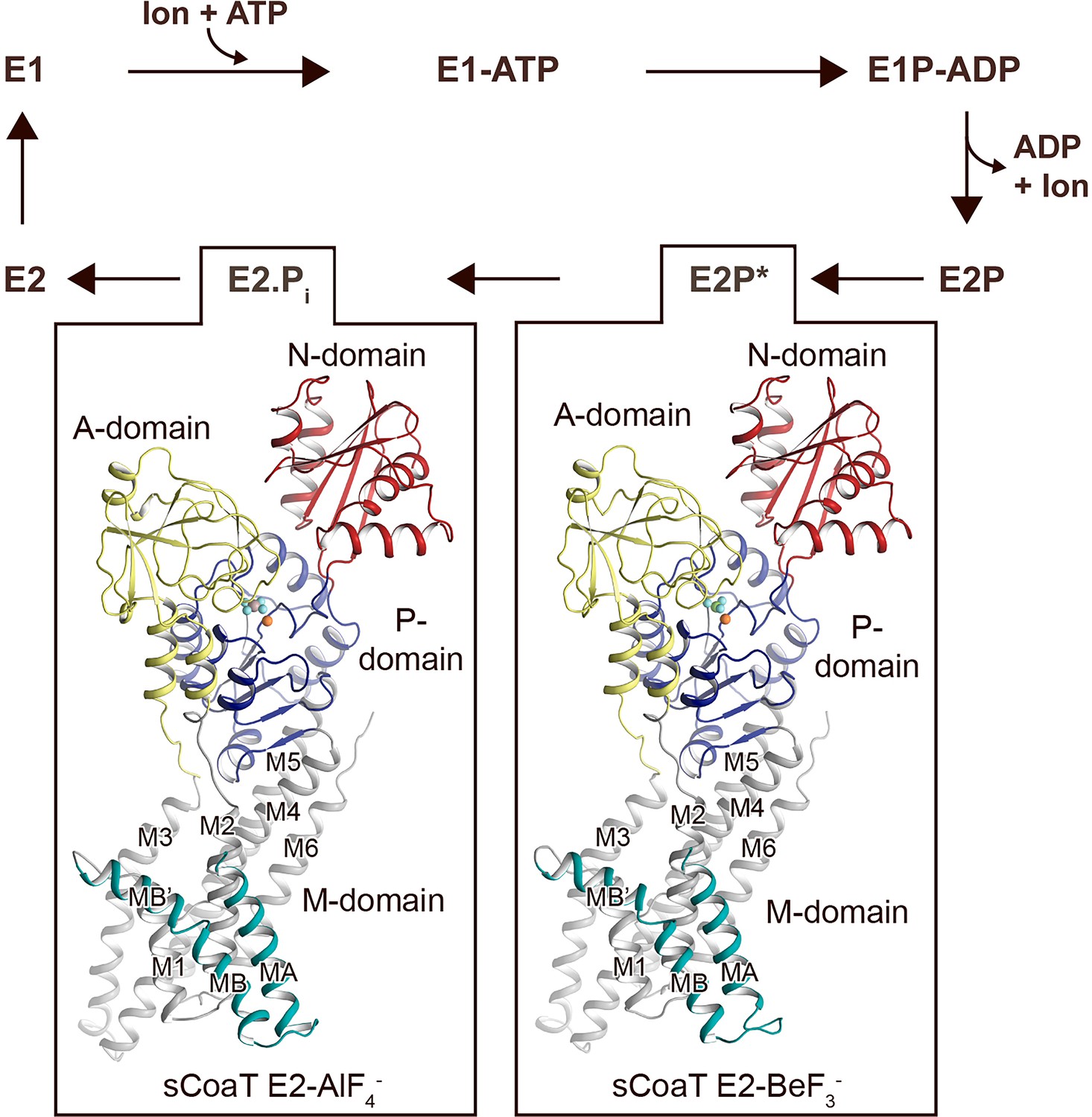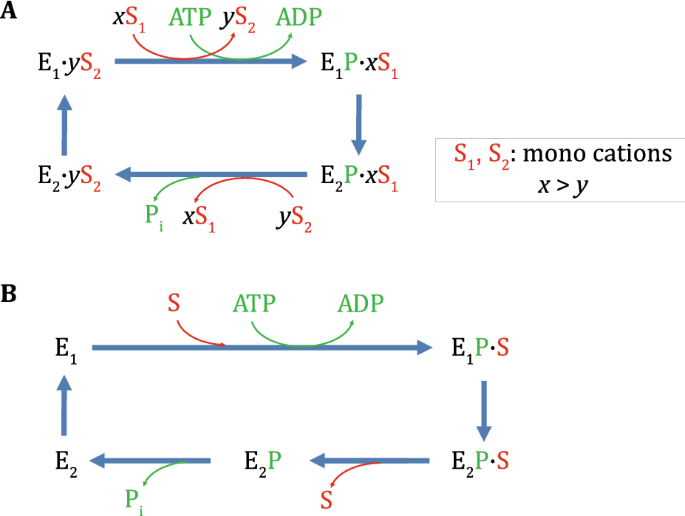
P-type ATPases use a domain-association mechanism to couple ATP hydrolysis to conformational change | SpringerLink

biochemistry - Difference between the P4 and P5 subtypes of P-type ATPases in plants - Biology Stack Exchange
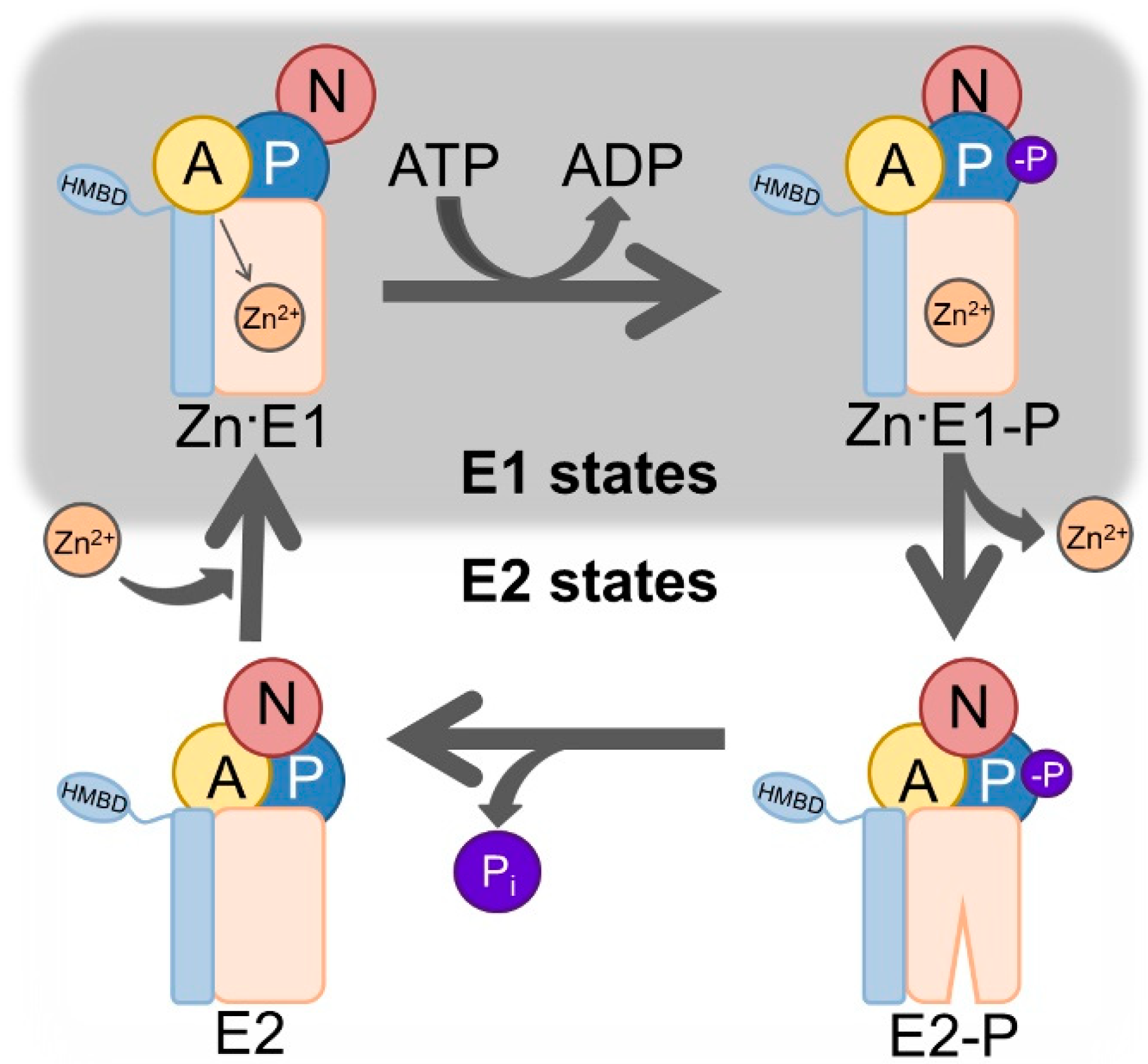
Antibodies | Free Full-Text | Isolation and Characterization of Nanobodies against a Zinc-Transporting P-Type ATPase
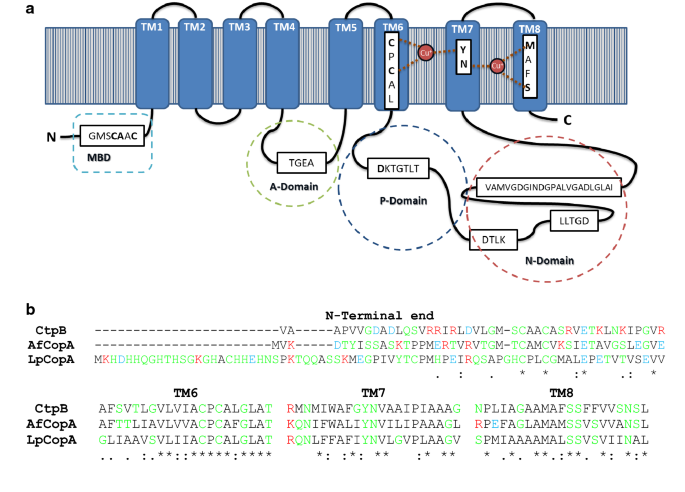
CtpB is a plasma membrane copper (I) transporting P-type ATPase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Biological Research | Full Text
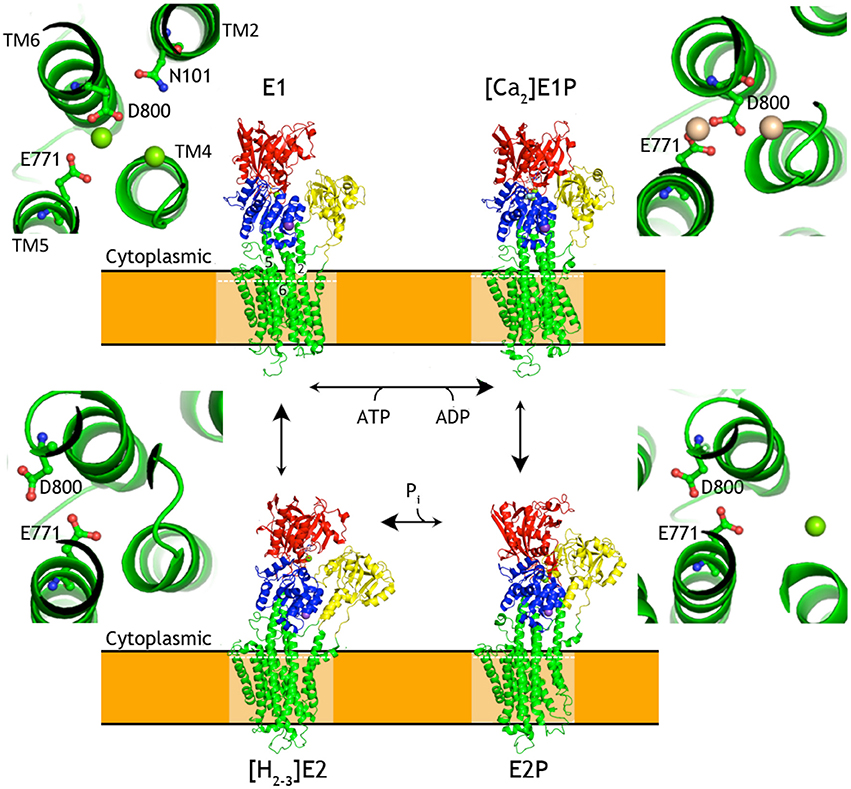
Frontiers | Improved Model of Proton Pump Crystal Structure Obtained by Interactive Molecular Dynamics Flexible Fitting Expands the Mechanistic Model for Proton Translocation in P-Type ATPases

F- TYPE ATPase|| V-TYPE PUMP ||ABC-TRANSPORTER||PRIMARY ACTIVE TRANSPORT||CSIR-NET||GATE||BARC||ICMR - YouTube

Copper-transporting P-type ATPases use a unique ion-release pathway | Nature Structural & Molecular Biology

ATPase Focused Libraries | Targeted and Focused Screening Libraries | Screening Libraries | Life Chemicals

The P5A ATPase Spf1p is stimulated by phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and influences cellular sterol homeostasis | Molecular Biology of the Cell