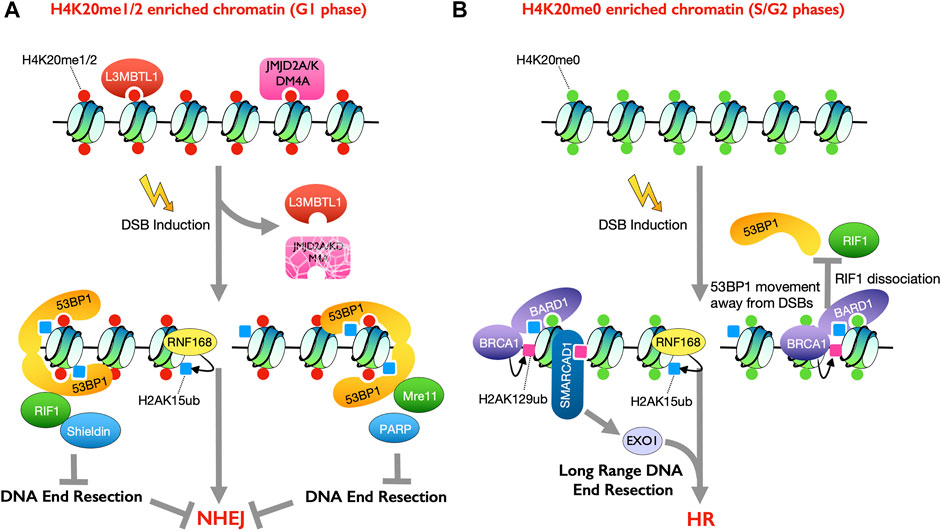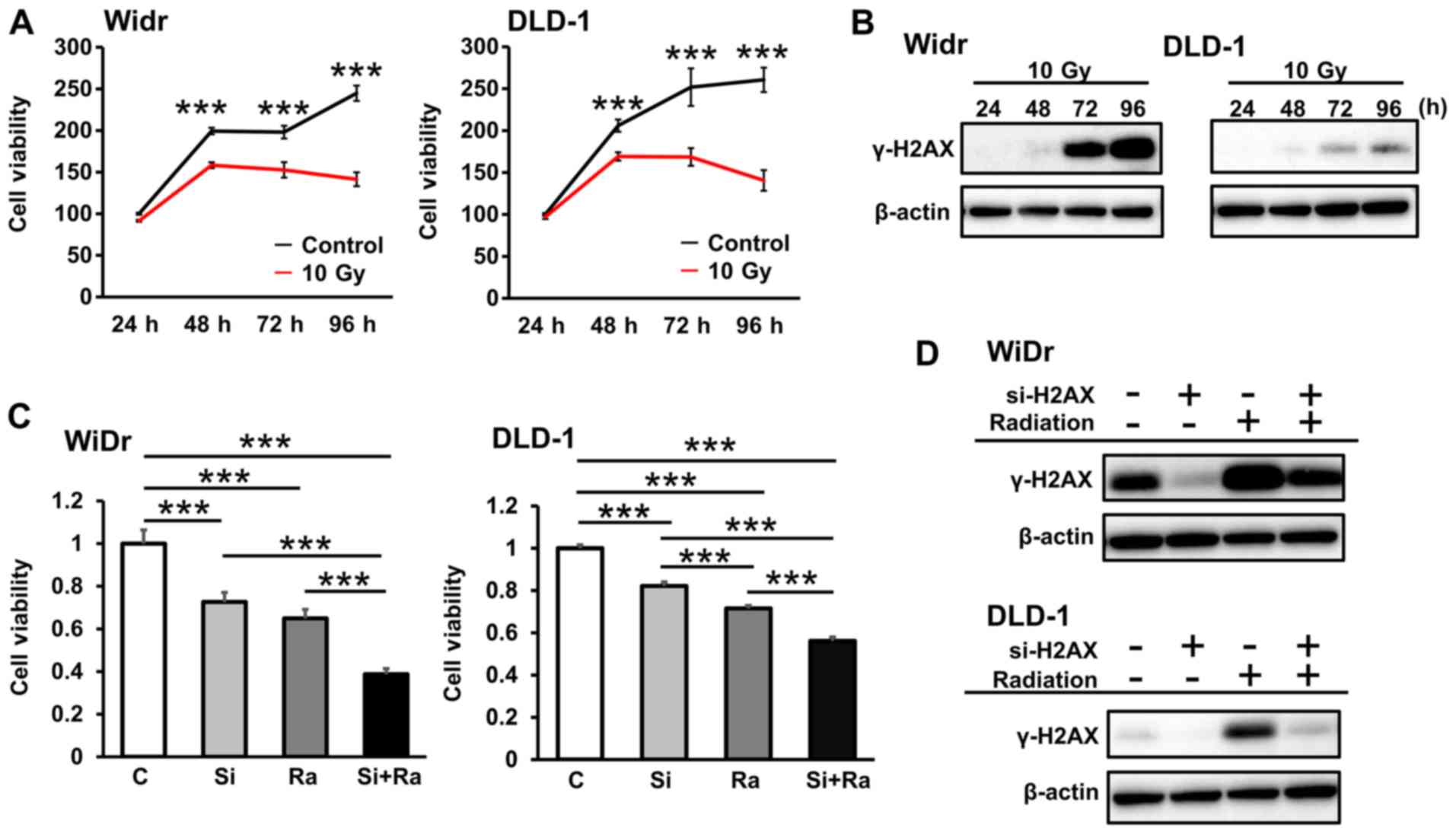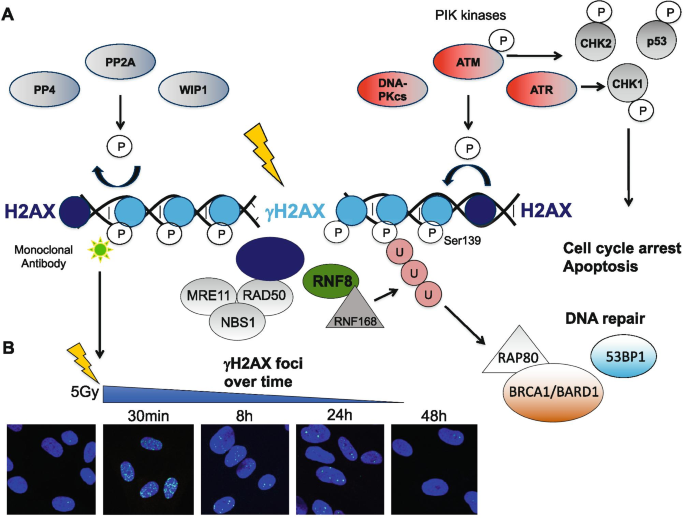
Biomarkers of DNA Damage Response Enable Flow Cytometry-Based Diagnostic to Identify Inborn DNA Repair Defects in Primary Immunodeficiencies | SpringerLink
![PDF] ROLE OF γ-H2AX IN DNA-DAMAGE RESPONSE AND ITS POSSIBLE CLINICAL APPLICATIONS | Semantic Scholar PDF] ROLE OF γ-H2AX IN DNA-DAMAGE RESPONSE AND ITS POSSIBLE CLINICAL APPLICATIONS | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/1c9c5c2d851ee6045154da8e492d9069695d210b/6-Figure2-1.png)
PDF] ROLE OF γ-H2AX IN DNA-DAMAGE RESPONSE AND ITS POSSIBLE CLINICAL APPLICATIONS | Semantic Scholar

Quantitative Analysis of H2A.X and ATM DNA Damage Signals Using Benchtop Flow Cytometry | American Laboratory
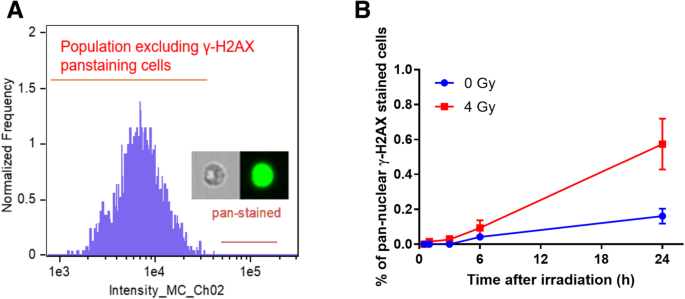
Development of a high-throughput γ-H2AX assay based on imaging flow cytometry | Radiation Oncology | Full Text

H2AX is a central component of numerous signalling pathways in response... | Download Scientific Diagram

High mobility group protein-mediated transcription requires DNA damage marker γ-H2AX | Cell Research

Cytometry of ATM activation and histone H2AX phosphorylation to estimate extent of DNA damage induced by exogenous agents - Tanaka - 2007 - Cytometry Part A - Wiley Online Library

Chronic oxidative stress promotes H2AX protein degradation and enhances chemosensitivity in breast cancer patients | EMBO Molecular Medicine
A role of the 53BP1 protein in genome protection: structural and functional characteristics of 53BP1-dependent DNA repair | Aging

Histone H2AX phosphorylation as a measure of DNA double-strand breaks and a marker of environmental stress and disease activity in lupus | Lupus Science & Medicine
![PDF] Measurement of H2AX Phosphorylation as a Marker of Ionizing Radiation Induced Cell Damage | Semantic Scholar PDF] Measurement of H2AX Phosphorylation as a Marker of Ionizing Radiation Induced Cell Damage | Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/7231129420b711b344287a31f248c7bf8c148267/8-Figure2-1.png)
PDF] Measurement of H2AX Phosphorylation as a Marker of Ionizing Radiation Induced Cell Damage | Semantic Scholar

Cancers | Free Full-Text | Uniform Widespread Nuclear Phosphorylation of Histone H2AX Is an Indicator of Lethal DNA Replication Stress
Use of the γ-H2AX Assay to Investigate DNA Repair Dynamics Following Multiple Radiation Exposures | PLOS ONE

Non-canonical Bromodomain within DNA-PKcs Promotes DNA Damage Response and Radioresistance through Recognizing an IR-Induced Acetyl-Lysine on H2AX - ScienceDirect

Immunofluorescence Microscopy of γH2AX and 53BP1 for Analyzing the Formation and Repair of DNA Double-strand Breaks | Protocol

Figure 4 from γ-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin | Semantic Scholar



![Recombinant Anti-Histone H2A.X antibody [EPR895] - Nuclear Marker (ab124781) Recombinant Anti-Histone H2A.X antibody [EPR895] - Nuclear Marker (ab124781)](https://www.abcam.com/ps/products/124/ab124781/Images/ab124781-237294-anti-histone-h2ax-antibody-epr895-chip-grade-western-blot.jpg)